Dove si trova la carotide sinistra?
Sommario
- Dove si trova la carotide sinistra?
- Quale la vena carotide?
- Dove passa la carotide interna?
- Cosa Vascolarizza l'arteria carotide interna?
- Cosa irrora la carotide esterna?
- Che differenza c'è tra giugulare e carotide?
- Come si fa l'intervento alla carotide?
- What are the carotid arteries?
- What attaches the tunica adventitia to the carotid artery?
- Where is the carotid sinus located?
- What are the variations of carotid artery bifurcation?
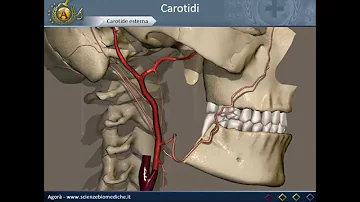
Dove si trova la carotide sinistra?
L'arteria carotide comune sinistra è divisa in due parti: una parte toracica (torace) e una parte cervicale (collo). La carotide comune destra ha origine nel o in prossimità del collo e contiene solo una piccola porzione toracica.
Quale la vena carotide?
Le carotidi sono due grandi vasi arteriosi del collo, le cui ramificazioni irrorano il sistema nervoso centrale e le strutture facciali. Si distinguno, rispettivamente, un'arteria carotide di destra ed un'arteria carotide di sinistra.
Dove passa la carotide interna?
L'arteria carotide interna è un grosso vaso che porta i suoi rami all'encefalo anteriore, alle leptomeningi, al globo oculare, alle strutture accessorie dell'occhio, oltre a portare branche arteriose al naso e alla fronte.
Cosa Vascolarizza l'arteria carotide interna?
L'arteria carotide è un grosso vaso sanguigno deputato a irrorare la testa e il collo. L'arteria carotide interna, in particolare, è responsabile della vascolarizzazione dell'encefalo, dell'occhio e dei suoi annessi, della fronte e di parte del naso.
Cosa irrora la carotide esterna?
La carotide esterna dà come rami collaterali l'arteria tiroidea superiore, l'arteria linguale, l'arteria faringea ascendente, l'arteria faciale, l'arteria occipitale e l'arteria auricolare posteriore, che irrorano i territori omonimi; i suoi rami terminali sono invece l'arteria temporale superficiale, che vascolarizza ...
Che differenza c'è tra giugulare e carotide?
Semplificando, la più grande differenza tra carotide e giugulare è che mentre l'arteria carotide porta sangue ossigenato dal cuore all'encefalo ed altre strutture della testa, invece la vena giugulare porta il sangue ricco di anidride carbonica da encefalo e strutture della testa verso il cuore.
Come si fa l'intervento alla carotide?
La chirurgia per il restingimento carotideo Generalmente l'intervento si realizza in anestesia locale. La carotide viene isolata ed aperta, in modo da poter rimuovere la placca. Vanno adottate delle opportune precauzioni per evitare che piccoli frammenti di placca vadano in circolo aumentando il rischio di trombosi.
What are the carotid arteries?
- The carotid arteries are the primary vessels supplying blood to the brain and face.[1][2] The right common carotid artery (RCCA) originates in the neck from the brachiocephalic artery while the left common carotid artery (LCCA) arises in the thorax from the arch of the aorta.[3]
What attaches the tunica adventitia to the carotid artery?
- The tunica adventitia attaches the carotid vessel to the surrounding tissue. The carotid arteries originate posterior to the sternoclavicular joints and in the neck, they are contained within the carotid sheath posterior to the sternocleidomastoid muscle.
Where is the carotid sinus located?
- The carotid sinus is a dilation at the base of the internal carotid artery. The nearby carotid body is a fibrous-covered structure that rests posteriorly to the carotid bifurcation. The blood supply to carotid sinus is by the vasa vasorum vessels.
What are the variations of carotid artery bifurcation?
- Anatomical Variations. Occasionally, the common carotid artery bifurcates at a higher level near the hyoid bone. More rarely, it bifurcates lower than usual at the level of the larynx. In very rare cases, the common carotid artery does not bifurcate, resulting in the absence of the external and internal carotid arteries.















