Come funzionano gli acceleratori?
Come funzionano gli acceleratori?
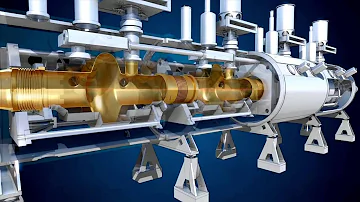
Il meccanismo su cui si basano gli acceleratori è lo stesso sia per gli elettroni sia per i protoni. In un tubo vengono messe in successione la sorgente di queste particelle usate come proiettili e alcune scatole metalliche di forma cilindrica, forate al centro di ogni base (figura in basso).
Come fanno ad accelerare le particelle?
Le particelle possono essere accelerate solo se sono cariche, perché per farlo si utilizzano dei campi elettrici. Si possono accelerare, ad esempio, i protoni, che hanno una carica elettrica positiva, o gli elettroni, che sono carichi negativamente.
Where is the Large Hadron Collider (LHC)?
- The accelerator sits in a tunnel 100 metres underground at CERN, the European Organization for Nuclear Research, on the Franco-Swiss border near Geneva, Switzerland. What is the LHC?
Why did CERN shut down the LHC?
- In March 2010 scientists at CERN announced that a problem with the design of superconducting wire in the LHC required that the collider run only at half-energy (7 TeV). The LHC was shut down in February 2013 to fix the problem and was restarted in April 2015 to run at its full energy of 13 TeV.
What is the power consumption of the LHC?
- For Run 2, the estimated power consumption is 750 GWh per year. The total CERN energy consumption is 1.3 TWh per year while the total electrical energy production in the world is around 20000 TWh, in the European Union 3400 TWh, in France around 500 TWh, and in Geneva canton 3 TWh. What are the main achievements of the LHC so far?
What is the difference between the CERN LHC and Isolde?
- The CERN accelerator complex accelerates protons, but also nuclei of ionized atoms (ions), such as the nuclei of lead, argon or xenon atoms. Some LHC runs are thus dedicated to lead-ion collisions. The ISOLDE facility accelerates beams of exotic nuclei for nuclear physics studies.















